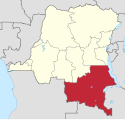
Staten Katanga
| Staten Katanga | ||||
| État du Katanga Inchi ya Katanga | ||||
| ||||
 |  | |||
| Flagga | Vapen | |||
 | ||||
| Huvudstad | Élisabethville | |||
| Språk | Franska Kikongo Swahili Luba-Kasai | |||
| Religion | Kristendom Baluba Bantu | |||
| Statsskick | Republik | |||
| Sista president | Moïse Tshombe | |||
| Bildades | 11 juli 1960 | |||
| – bildades genom | Bröt sig ur Republiken Kongo | |||
| – bildades ur | Republiken Kongo | |||
| Upphörde | 15 januari 1963 | |||
| – upphörde genom | FN-soldater återtog kontrollen över Élisabethville | |||
| – uppgick i | Republiken Kongo | |||
| Areal | 496 871 km² | |||
| Valuta | Katangesisk franc | |||
| Idag del av | ||||

Staten Katanga var en kortlivad utbrytarstat ur Kongo-Léopoldville (Republiken Kongo) under Kongokrisen åren 1960–1963.[1] Staten Katanga utropades den 11 juli 1960 när provinsen Katanga bröt sig ut ur den nybildade Republiken Kongo och förklarade sig självständig. Dess suveränitet erkändes aldrig av någon annan nation men stöddes de facto av den forna kolonialmakten Belgien som hade starka ekonomiska intressen i Katangas koppargruvor i form av gruvbolaget Union Minière du Haut Katanga. Koppar var Katangas främsta naturtillgång och var helt avgörande för den nybildade Republiken Kongos ekonomi. Belgien hade även en stor inofficiell militär närvaro i Katanga under större delen av dess existens. Staten Katanga leddes av Moïse Tshombe.
Källor
- Denna artikel är helt eller delvis baserad på material från Engelskspråkiga Wikipedia.
Fotnoter
- ^ ”Katanga” (på engelska). World Statesmen. http://www.worldstatesmen.org/Congo-K_Provinces_1960-1966.html#Katanga. Läst 3 december 2016.
Media som används på denna webbplats
En bild som används för att markera saknade flaggor, som ett alternativ för visning av blanksteg.
Författare/Upphovsman: Derivative work: User:Profoss - Original work:Uwe Dedering, Licens: CC BY-SA 3.0
Location of Province (see file name) in Democratic Republic of the Congo
Flag of State of Katanga (1960–1963). This digital reproduction has its design (dimensions 3:4), all four crosses (arms have same length and are coloured red; called "croisettes" in Katanga) and colours ("rouge vermilion", "vert clair" and "blanc") based on Katanga / Shaba (Democratic Republic of Congo) (FOTW), Neue Publikation: Katanga (1960/63) at www.flaggenkunde.de and the official regulations concerning the Katangese flag. According to these sources, the flag was designed by an architect named Louis Dressen. The flag was introduced on 1960-07-18 and ratified by the national assembly on 1960-07-28 and remained until its last usage on 1963-05-24. During its short existence, the flag had many variations, primarily in the design and colour of the three crosses. Secondary sources included Self-proclaimed states in the Congo 1960-1963 (flag), Katanga 10 Francs ND (1960) (obverse side of banknote located at banknotes_com/KAT5AR.JPG), Repubblica del Katanga, République du Katanga, fino al 1871 (www.rbvex.it), Republic of Katanga - 1961 - Drapeau du Katanga, Gendarmerie Katangaise, The Republic of Katanga Mining Projects and Histoire de l'Independance de la Republic du Katanga.
Coat of arms of State of Katanga (1960-1963). This digital reproduction was based on the File:Flag of Katanga.svg and inspired by the following primary sources: Etat Secessionniste Du Katanga (1960-1963), Rhodesian insignia, also Arab Legion, UN Medal, Katanga, Biafra and S. African Police Reaction Unit patch (www.warbooks.com), Ambulance mitraillée par les soldats de PONU (page 235) and [http://www.ngw.nl/int/afr/katanga.htm Civic Heraldry of Congo (former Zaire) (www.ngw.nl) - Katanga State]. the flag was designed by an architect named Louis Dressen. The flag was introduced on 1960-07-18 and ratified by the national assembly on 1960-07-28, remaining until its last usage on 1963-05-24. During its short existence, the flag had many variations, primarily in its design and colour of the three crosses.