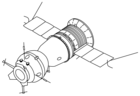
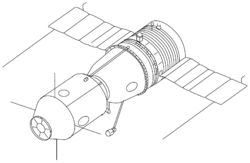
Sojuz TMA-1
| Sojuz TMA-1 (Союз ТMA-1) | |||
 | |||
| Beställare | Roskosmos | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Modell | Sojuz-TMA | ||
| Tillverkare | RKK Energia | ||
| Operatör | Roskosmos | ||
| Anrop | Yenisey | ||
| Färdens tid | 185 dag, 22 tim, 53 min, 14 sek | ||
| NSSDC-ID | 2002-050A[1] | ||
| Uppskjutning | |||
| Startplats | Bajkonur LC1 | ||
| Start | 30 oktober 2002, 03:11:11 UTC | ||
| Raket | Sojuz-FG | ||
| Landning | |||
| Landningsplats | Kazakstan | ||
| Landning | 4 maj 2003, 02:04:25 UTC | ||
| Omloppsbana | |||
| Varv | 3 020 st[2] | ||
| Apogeum | 235 km | ||
| Perigeum | 193 km | ||
| Banlutning | 51,6° | ||
| Besättning | |||
| Start | Sergei Zaljotin (2) Frank De Winne (1) Jurij Lontjakov (2) | ||
| Landning | Nikolai Budarin (3) Kenneth Bowersox (5) Donald Pettit (1) | ||
 V-H: de Winne, Zaljotin, Lontjakov | |||
| Dockning | |||
| Rymdstation | ISS | ||
| Dockning | 1 november 2002, 05:01:20 UTC | ||
| Port | Pirs, nadir | ||
| Ur dockning | 3 maj 2003, 22:43:00 UTC | ||
| Kronologi | |||
| |||
Sojuz TMA-1 (ryska: Союз ТMA-1) var en flygning i det ryska rymdprogrammet. Flygningen gick till Internationella rymdstationen. Farkosten sköts upp från Kosmodromen i Bajkonur med en Sojuz-FG-raket, den 30 oktober 2002. Man dockade med rymdstationen den 1 november 2002.
Man lämnade rymdstationen den 3 maj 2003. Några timmar senare återinträdde den i jordens atmosfär och landade i Kazakstan.
I och med att farkosten lämnade rymdstationen var Expedition 6 avslutad.
Flygningen var den första med en Sojuz av modell TMA.
Vid återinträdet blev banan ballistisk och landningen skedde därför utanför den planerade landningszonen.
Källor och referenser
- ^ ”NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive” (på engelska). NASA. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=2002-050A. Läst 29 februari 2020.
- ^ Manned Astronautics - Figures & Facts Arkiverad 9 maj 2016 hämtat från the Wayback Machine., läst 9 oktober 2016.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Media som används på denna webbplats
The civil ensign and flag of Belgium. It is identical to Image:Flag of Belgium.svg except that it has a 2:3 ratio, instead of 13:15.
View of Soyuz 5 crew Belgian Flight Engineer Frank DeWinne left, of the European Space Agency ESA, Cosmonaut Soyuz Commander Sergei Zalyotin center and Cosmonaut Yuri Lonchakov, Flight Engineer in the Service Module SM/Zvezda during Expedition Five on the International Space Station ISS.
Soyuz-TM spacecraft. Compare the antennas on the orbital module to those on Soyuz-T. Differences reflect the change from the Igla rendezvous system used on Soyuz-T to the Kurs rendezvous system used on Soyuz-TM.
Författare/Upphovsman: Flappiefh, Licens: CC BY-SA 3.0
Logo of the Soyouz TMA-1 mission
In this illustration, a SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft approaches the International Space Station for docking. NASA is partnering with Boeing and SpaceX to build a new generation of human-rated spacecraft capable of taking astronauts to the station and expanding research opportunities in orbit. SpaceX's upcoming Demo-1 flight test is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability contract with the goal of returning human spaceflight launch capabilities to the United States.
Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) Soyuz. The APAS-75 docking unit is located at left.
The Soyuz TMA-04M spacecraft is seen after being rolled out by train to the launch pad at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, May 13, 2012. The launch of the Soyuz spacecraft, with Expedition 31 Soyuz Commander Gennady Padalka, Flight Engineer Sergei Revin of Russia and NASA Flight Engineer Joe Acaba, is scheduled for 9:01 a.m., May 15 (Kazakhstan time).
Författare/Upphovsman: Pascal (Flickr user: pasukaru76), Licens: CC0
Vostok spacecraft replica at the Technik Museum Speyer, Germany.
Official patch for the Soyuz TMA-2 mission, carrying Expedition 7 to the International Space Station.
Backdropped by a blue and white Earth, this close-up view features the Soyuz TMA-6 spacecraft approaching the International Space Station (ISS). Onboard the spacecraft are cosmonaut Sergei K. Krikalev, Expedition 11 commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency; astronaut John L. Phillips, NASA ISS science officer and flight engineer; and European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Roberto Vittori of Italy. The Soyuz linked to the Pirs Docking Compartment at 9:20 p.m. (CDT) on April 16, 2005 as the two spacecraft flew over eastern Asia. The docking followed Friday’s launch from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan.
Rotated and color enhanced version of original (ISS013-E-48788 (6 July 2006) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery approaches the International Space Station for docking but before the link-up occurred, the orbiter went through a series of inspection photos by station crew to inspect the vehicle for any damage to its Thermal Protection System. This was known as the Rendezvous Pitch Maneuver and was implemented after the Columbia Disaster in 2003. The Leonardo Multipurpose Logistics Module can be seen in the shuttle's cargo bay. Discovery docked at the station's Pressurized Mating Adapter 2 at 9:52 a.m. CDT, July 6, 2006.)
Insignia for the Soyuz TM-34 mission to the International Space Station. In this version: Converted to PNG format, background removed, and other minor optimizations.
Soyuz-A manned spacecraft concept (1963). It was to have been part of the Soyuz A-B-C circumlunar complex.