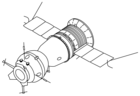
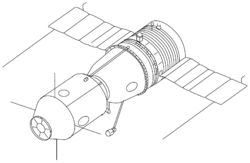
Sojuz TM-26
| Sojuz TM-26 (Союз ТM-26) | |||
 | |||
| Modell | Sojuz-TM | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Anrop | Родни́к (Rodnik - Källa) | ||
| Färdens tid | 197 dag, 17 tim, 34 min, 36 sek[1] | ||
| Massa | 7 150 kg | ||
| NSSDC-ID | 1997-038A[2] | ||
| Uppskjutning | |||
| Startplats | Bajkonur LC1 | ||
| Start | 5 augusti 1997, 15:35:54 UTC | ||
| Raket | Sojuz-U | ||
| Landning | |||
| Landning | 19 februari 1998, 09:10:30 UTC | ||
| Omloppsbana | |||
| Varv | 3 220 st[1] | ||
| Apogeum | 249 km | ||
| Perigeum | 193 km | ||
| Banlutning | 51,6° | ||
| Besättning | |||
| Start | Anatolij J. Solovjev Pavel Vinogradov | ||
| Landning | Anatolij J. Solovjev Pavel Vinogradov Léopold Eyharts | ||
| Dockning | |||
| Rymdstation | Mir | ||
| Dockning | 7 augusti 1997, 17:02:07 UTC | ||
| Port | Kvant-1 | ||
| Ur dockning | 15 augusti 1997, 13:29:20 UTC | ||
| Andra Dockning | 15 augusti 1997, 14:13:04 UTC | ||
| Port | fram | ||
| Andra ur dockning | 19 februari 1998, 05:52:19 UTC | ||
| Kronologi | |||
| |||
Sojuz TM-26 (ryska: Союз ТM-26) var en flygning i det ryska rymdprogrammet. Flygningen gick till rymdstationen Mir. Farkosten sköts upp med en Sojuz-U-raket, från Kosmodromen i Bajkonur den 5 augusti 1997. Den dockade med rymdstationen den 7 augusti 1997.
Den 15 augusti 1997 flyttades farkosten från Kvant-1-modulens dockningsport till rymdstationens främre dockningsport.
Farkosten lämnade rymdstationen den 19 februari 1998. Några timmar senare återinträdde den i jordens atmosfär och landade i Kazakstan.
Målet med flygningen var att transportera Solovjev och Vinogradov som tränats för reparations arbete, till Mir.

Källor och referenser
- ^ [a b] Manned Astronautics - Figures & Facts Arkiverad 26 september 2015 hämtat från the Wayback Machine., läst 21 augusti 2016.
- ^ ”NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive” (på engelska). NASA. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=1997-038A. Läst 29 februari 2020.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Media som används på denna webbplats
Soyuz-A manned spacecraft concept (1963). It was to have been part of the Soyuz A-B-C circumlunar complex.
Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) Soyuz. The APAS-75 docking unit is located at left.
Soyuz-TM spacecraft. Compare the antennas on the orbital module to those on Soyuz-T. Differences reflect the change from the Igla rendezvous system used on Soyuz-T to the Kurs rendezvous system used on Soyuz-TM.
The Soyuz TMA-04M spacecraft is seen after being rolled out by train to the launch pad at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, May 13, 2012. The launch of the Soyuz spacecraft, with Expedition 31 Soyuz Commander Gennady Padalka, Flight Engineer Sergei Revin of Russia and NASA Flight Engineer Joe Acaba, is scheduled for 9:01 a.m., May 15 (Kazakhstan time).
Författare/Upphovsman: Pascal (Flickr user: pasukaru76), Licens: CC0
Vostok spacecraft replica at the Technik Museum Speyer, Germany.
MIR Space Station Emblem
The damaged solar array of the Spektr module following the collision between Mir and the Progress M-34 freighter on 25 June 1997.
The official crew patch for the Russian Soyuz TM-27 mission, which delivered the EO-25 and Pegasé crews to the space station Mir.
The official crew patch for the Russian Soyuz TM-25 mission, which delivered the EO-23 crew to the space station Mir.
The official crew patch for the Russian Soyuz TM-26 mission, which delivered the EO-24 crew to the space station Mir.