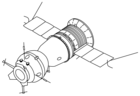
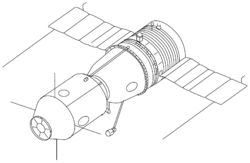
Kosmos 1074
| Kosmos 1074 (Космос-1074) | |
| Modell | Sojuz-T |
|---|---|
| Massa | 6 450 kg |
| NSSDC-ID | 1979-008A[1] |
| Uppskjutning | |
| Startplats | Bajkonur 31/6 |
| Start | 31 januari 1979, 09:07 UTC |
| Raket | Sojuz |
| Landning | |
| Landning | 1 april 1979, 12:02 UTC |
| Omloppsbana | |
| Apogeum | 258 km |
| Perigeum | 203 km |
| Banlutning | 51.6° |
Kosmos 1074 (ryska: Космос-1074) var en obemannad flygning i det sovjetiska rymdprogrammet. Flygningen var ett långtidstest av Sojuz-T. Farkosten sköts upp med en Sojuz-raket, från Kosmodromen i Bajkonur, den 31 januari 1979.
Farkosten återinträdde i jordens atmosfär och landade i Sovjetunionen den 1 april 1979.
Källor och referenser
- ^ ”NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive” (på engelska). NASA. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=1979-008A. Läst 28 februari 2020.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Media som används på denna webbplats
Soyuz-A manned spacecraft concept (1963). It was to have been part of the Soyuz A-B-C circumlunar complex.
Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) Soyuz. The APAS-75 docking unit is located at left.
Soyuz-TM spacecraft. Compare the antennas on the orbital module to those on Soyuz-T. Differences reflect the change from the Igla rendezvous system used on Soyuz-T to the Kurs rendezvous system used on Soyuz-TM.
The Soyuz TMA-04M spacecraft is seen after being rolled out by train to the launch pad at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, May 13, 2012. The launch of the Soyuz spacecraft, with Expedition 31 Soyuz Commander Gennady Padalka, Flight Engineer Sergei Revin of Russia and NASA Flight Engineer Joe Acaba, is scheduled for 9:01 a.m., May 15 (Kazakhstan time).