Federal Reserve Bank of New York
| Federal Reserve Bank of New York | |
 | |
 Huvudkontoret för Federal Reserve Bank of New York i april 2015. | |
| Typ | Centralbankssystem |
|---|---|
| Huvudkontor | 33 Liberty Street New York, USA |
| Nyckelpersoner | Vincent Alvarez Styrelseordförande John C. Williams President VD Sushmita Shukla Förste vicepresident COO |
| Bransch | Bank & finans |
| Produkter | Ekonomisk politik Finansiell ekonomi Penningpolitik |
| Antal anställda | 2 958 – 2023 |
| Historik | |
| Grundat | 18 maj 1914 |
| Grundare | Federal Reserve System |
| Ekonomi | |
| Omsättning | ▲ $ 91,281 miljarder |
| Överfört till USA:s finansdepartement | ▼ $ −72,66 miljarder |
| Vinst efter skatt | ▲ $ 272,152 miljoner |
| Tillgångar | ▼ $ 4,148 biljoner |
| Eget kapital | ▼ $ 14,815 miljarder |
| Struktur | |
| Moderbolag | Federal Reserve System |
| Övrigt | |
| Slogan | Serving the second district and the nation. |
| Webbplats | NewYorkFed.org |
| Fotnoter | Statistik från 2023 års bokslut.[1] |

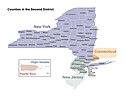
Federal Reserve Bank of New York, kallas New York Fed, är en av de tolv Federal Reserve Bank-bankerna i USA. Det är en privat bank och dess kontor ligger på 33 Liberty Street i New York i New York. Banken har en särställning av Federal Reserve-bankerna eftersom den har överlägset störst tillgångar, omsättning (handel) och makt. Federal Reserve Bank of New York är ansvarig för att implementera USA:s monetära policy, vilket görs genom "öppna marknadsoperationer", för att övervaka och reglera de finansiella institutionerna i landet[2] och för att landets penningsystem fungerar.[3] Dessutom ansvarar banken för det andra distriktet i Federal Reserve System, som inkluderar delstaten New York; de 12 nordligaste countyna i New Jersey; Fairfield County i Connecticut; Puerto Rico samt Amerikanska jungfruöarna.[4]
New York Fed använder sig av bokstaven B och siffran 2 för att identifiera sig på de dollar-sedlar som används i distriktet.[5]
Historik
Federal Reserve System har sitt ursprung från den 23 december 1913 när lagen Federal Reserve Act signerades av USA:s 28:e president Woodrow Wilson (D).[6] Den 2 april 1914 meddelade Federal Reserve System att distrikten var bestämda och vart de regionala centralbankerna skulle vara placerade.[7] Den 18 maj grundades samtliga tolv regionala centralbanker[8] medan den 16 november öppnades dessa officiellt[9].
Den största regionala Federal Reserve-banken
Sedan Federal Reserve-systemet grundades har Federal Reserve Bank of New York ansvarat för att den monetära politiken genomförs, även om besluten tas i Washington D.C. av Federal Reserves styrelse Board of Governors. Banken är ansvarig för öppna marknadsoperationer, det vill säga att köpa och sälja utstående statsobligationer. Ansvaret att upprätthålla en "lagom" nivå på växelkursen mellan dollar och andra valutor, genom att köpa och sälja dollar, ligger också på Federal Reserve Bank of New York. Dessutom är banken den enda av de regionala Fed-bankerna som har en permanent röst i Federal Open Market Committee och dess president väljs i allmänhet till kommitténs vice ordförande.
33 Liberty Street
Federal Reserve Bank of New York har ritats av arkitektfirman York and Sawyer, som vann den arkitekttävling som föregick byggnationen. 1924 flyttades banken till dess nuvarande plats.[10] Banken har ett stort innehav av guldreserver, möjligen störst i världen (även om detta inte kan konfirmeras genom att schweiziska banker inte rapporterar sitt guldinnehav).
Ledare
Källa: [11]
* = Ordförande för Federal Reserve System.
| Person | Period | |
|---|---|---|
| Bankchefer | ||
 | Benjamin Strong Jr. | 1914–1928 |
 | George L. Harrison | 1928–1936 |
| Presidenter | ||
 | George L. Harrison | 1936–1940 |
| Allan Sproul | 1940–1956 | |
| Alfred Hayes | 1956–1975 | |
 | Paul A. Volcker* | 1975–1979 |
| Anthony M. Solomon | 1980–1985 | |
 | E. Gerald Corrigan | 1985–1993 |
 | William J. McDonough | 1993–2003 |
| Jamie B. Stewart | ||
 | Timothy F. Geithner | 2003–2009 |
 | William C. Dudley | 2009–2018 |
 | John C. Williams | 2018– |
Referenser
- ^ ”110th Annual Report of the board of governors of the Federal Reserve System”. Federal Reserve System. https://www.federalreserve.gov/publications/files/2023-annual-report.pdf. Läst 18 september 2024.
- ^ "The Great American Bubble Machine" Arkiverad 6 april 2010 hämtat från the Wayback Machine. p. 6 of 7, by Matt Taibbi, Rolling Stone, July 13, 2009 1:49 PM. Retrieved 2010-03-30.
- ^ "About the Fed." New York Federal Reserve Web page. Footnote upgraded/confirmed 2010-03-30.
- ^ ”What we do”. Federal Reserve Bank of New York. https://www.newyorkfed.org/aboutthefed/whatwedo.
- ^ ”Banknote identifiers and symbols: Federal Reserve indicators”. U.S. Currency Education Program. https://www.uscurrency.gov/denominations/bank-note-identifiers.
- ^ ”Federal Reserve Act signed by President Wilson”. Federal Reserve History. https://www.federalreservehistory.org/essays/federal_reserve_act_signed.
- ^ ”Reserve Bank Organization Committee announces selection of Reserve Bank cities and district boundaries”. Federal Reserve History. https://www.federalreservehistory.org/essays/reserve_bank_organization_committee.
- ^ Johnson, Roger T. ”Historical beginnings...the Federal Reserve”. Federal Reserve Bank of Boston. https://www.bostonfed.org/-/media/Documents/education/pubs/begin.pdf.
- ^ ”Reserve Banks open for business”. Federal Reserve History. https://www.federalreservehistory.org/essays/reserve_banks_open.
- ^ "History". New York Federal Reserve Webbsida. Hämtad 2010-03-30.
- ^ ”Timeline: Presidents of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York”. Federal Reserve Bank of Saint Louis. https://fraser.stlouisfed.org/timeline/presidents-frb-newyork.
Externa länkar
- Officiell webbplats
- "How Uncle Sam Guards His Millions", 31 mars 1931, Popular Mechanics, artikel om guldet vid Federal Reserve
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Media som används på denna webbplats
William C. Dudley, president of Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
Seal of the United States Federal Reserve System.
The seal has most of the elements of the Board of Governors seal. A version is printed on all U.S. Federal Reserve Notes redesigned since 1996 (replacing the letter of the bank which printed the note, which was used in earlier designs).Portrait of Benjamin Strong, Jr.
Current and Former FRB New York Presidents (Left to Right: William McDonough; William C. Dudley; Paul A. Volcker; E. Gerald Corrigan; Timothy F. Geithner)
Författare/Upphovsman: Public Domain, Licens: CC0
seal of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York
Current and Former FRB Minneapolis Presidents (Left to Right: Narayana R. Kocherlakota; E. Gerald Corrigan; Gary H. Stern)
Författare/Upphovsman: Beyond My Ken, Licens: CC BY-SA 4.0
The Federal Reserve Bank of New York Building at 33 Liberty Street as seen from the west.
This image of George L. Harrison, one-time chief executive of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, later president of New York Life Insurance Company and assistant to Secretary of War Henry L. Stimson during World War II, was obtained from the web site of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York [1] and is therefore presumed to be in the public domain.
NY Federal Reserve Bank President John C. Williams