Aspergillus fumigatus
| Den här artikeln har skapats av Lsjbot, ett program (en robot) för automatisk redigering. (2012-10) Artikeln kan innehålla fakta- eller språkfel, eller ett märkligt urval av fakta, källor eller bilder. Mallen kan avlägsnas efter en kontroll av innehållet (vidare information) |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | |
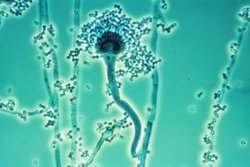 | |
| Systematik | |
|---|---|
| Domän | Eukaryoter Eukaryota |
| Rike | Svampar Fungi |
| Division | Sporsäcksvampar Ascomycota |
| Klass | Eurotiomycetes |
| Ordning | Eurotiales |
| Familj | Trichocomaceae |
| Släkte | Aspergillus |
| Art | Aspergillus fumigatus |
| Vetenskapligt namn | |
| § Aspergillus fumigatus | |
| Auktor | Fresen. 1863 |
| Synonymer | |
| Neosartorya fumigata C.M. O'Gorman, H.T. Fuller & P.S. Dyer 2009[1] | |
Aspergillus fumigatus är en svampart[2] som beskrevs av Fresen. 1863. Aspergillus fumigatus ingår i släktet Aspergillus och familjen Trichocomaceae.[3][4]
Underarter
Arten delas in i följande underarter:[3]
- helvolus
- acolumnaris
- ellipticus
- (c) Jankaan, CC BY-SA 3.0
Källor
- ^ C.M. O'Gorman, H.T. Fuller & P.S. Dyer (2009) , In: Nature, Lond. 457(no. 7228):473
- ^ Fresenius (1863) , In: Beitr. Mykol. 3:81
- ^ [a b] Bisby F.A., Roskov Y.R., Orrell T.M., Nicolson D., Paglinawan L.E., Bailly N., Kirk P.M., Bourgoin T., Baillargeon G., Ouvrard D. (red.) (1 augusti 2011). ”Species 2000 & ITIS Catalogue of Life: 2011 Annual Checklist.”. Species 2000: Reading, UK. http://www.catalogueoflife.org/annual-checklist/2011/search/all/key/aspergillus+fumigatus/match/1. Läst 24 september 2012.
- ^ Species Fungorum. Kirk P.M., 2010-11-23
 Wikimedia Commons har media som rör Aspergillus fumigatus.
Wikimedia Commons har media som rör Aspergillus fumigatus.
|
Media som används på denna webbplats
Robot icon
Författare/Upphovsman: 2011MMG320group3, Licens: CC BY-SA 3.0
The transcription factor LaeA regulates genes involved in secondary metabolite production in aspergillus.
(c) Jankaan, CC BY-SA 3.0
kolonie van Aspergillus fumigatus (macroscopie, schimmel)
eigen werkThe conidiophore of the fungal organism Aspergillus fumigatus
PHIL ID#: 10523
Description: This photomicrograph revealed the presence of Aspergillus fumigatus fungal organisms in a brain tissue, methenamine silver-stained specimen harvested from a turkey poult that had contracted this infection. What it Aspergillus?
Aspergillus is a fungus (or mold) that is very common in the environment. It is found in soil, on plants and in decaying plant matter. It is also found in household dust, building materials, and even in spices and some food items. There are lots of different types of Aspergillus, but the most common ones are Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus flavus. Some others are Aspergillus terreus, Aspergillus nidulans, and Aspergillus niger.
What is aspergillosis?
Aspergillosis is disease cause by Aspergillus. There are many different kinds of aspergillosis. One kind is allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (also called ABPA), a condition where the fungus causes allergic respiratory symptoms, such as wheezing and coughing, but does not actually invade and destroy tissue. Another kind of aspergillosis is invasive aspergillosis, a disease that usually affects people with immune system problems. In this condition, the fungus invades and damages tissues in the body. Invasive aspergillosis most commonly affects the lungs, but can also cause infection in many other organs and can spread throughout the body.Författare/Upphovsman: Dr. David Midgley, Licens: CC BY-SA 2.5
Aspergillus fumigatus from soil in culture.
ID#: 300 Description: Conidia: phialoconidia of Aspergillus fumigatus
Copyright Restrictions: None - This image is in the public domain and thus free of any copyright restrictions. As a matter of courtesy we request that the content provider be credited and notified in any public or private usage of this image.Conidiophores of Aspergillus. It may be Aspergillus fumigatus. Source: US Department of Health and Human Services, Center for disease control [1].
Författare/Upphovsman: Scott G. Filler, Donald C. Sheppard, Licens: CC BY 2.5
This is a cartoon depicting the invasion of Aspergillus fumigatus through the alveolar epithelium and into the vascular endothelium.
















