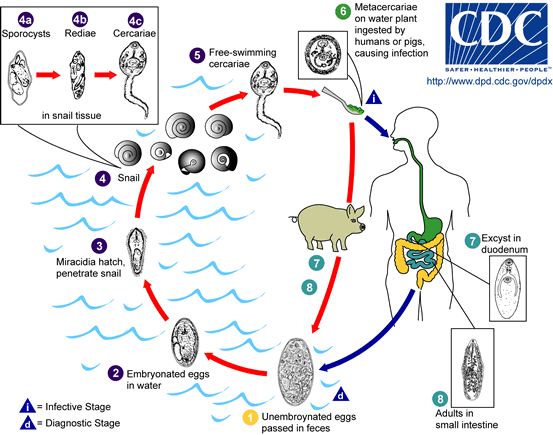
Fasciolopsis buski LifeCycle
Causal Agent: The trematode Fasciolopsis buski, the largest intestinal fluke of humans.
Life cycle of Fasciolopsis buski
Immature eggs are discharged into the intestine and stool . Eggs become embryonated in water , eggs release miracidia , which invade a suitable snail intermediate host . In the snail the parasites undergo several developmental stages (sporocysts , rediae , and cercariae ). The cercariae are released from the snail and encyst as metacercariae on aquatic plants . The mammalian hosts become infected by ingesting metacercariae on the aquatic plants. After ingestion, the metacercariae excyst in the duodenum and attach to the intestinal wall. There they develop into adult flukes (20 to 75 mm by 8 to 20 mm) in approximately 3 months, attached to the intestinal wall of the mammalian hosts (humans and pigs) . The adults have a life span of about one year.
Geographic Distribution:
Asia and the Indian subcontinent, especially in areas where humans raise pigs and consume freshwater plants.Mer information om licensen för bilden finns här. Senaste uppdateringen: Fri, 20 Sep 2024 02:04:38 GMT